- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
2017 AP Physics C物理C—Mechanics力学真题系列之Practice Exam简答题免费下载
历年AP Physics物理学系列
真题与答案下载

翰林国际教育全网首发
力争超快速发布最全资料
助你在升学路上一帆风顺
为你的未来保驾护航
2017 AP Physics C Mechanics Practice Exam Free-Response Questions Free Download
2017 AP 物理C力学模考简答题部分免费下载
此套题仅 p II含有简答题,
共计时45分钟,共3题
占总分50%
每道大题可能含有不同数量的小题
可以使用计算器
部分真题预览:
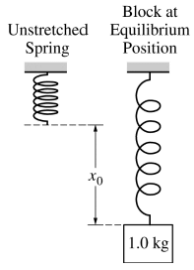
1)A spring of negligible mass and with a spring constant of 50 N/m is hung vertically, as shown above in the figure on the left. A block of mass 1.0 kg is attached to the spring and slowly lowered a distance x0 until it hangs at rest at the equilibrium position, as shown above in the figure on the right.
On the dot below that represents the block, draw and label the forces (not components) that act on the block when it is at the equilibrium position shown. Each force must be represented by a distinct arrow starting on, and pointing away from, the dot.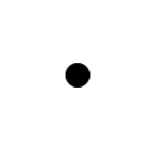
Calculate the distance x0 that the spring is stretched from its original length to the equilibrium position.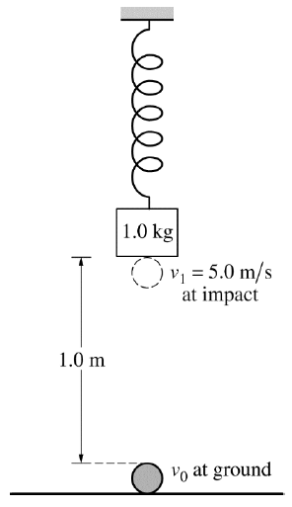
While the 1.0 kg block is in equilibrium, a 0.20 kg ball of clay is launched with speed v0 vertically from the ground 1.0 meter below the hanging block. The clay has speed v1 = 5.0 m/s when it collides with the block.
Calculate the speed v0 .
Upon impact, the clay sticks to the 1.0 kg block.
- Calculate the speed of the block immediately after the collision.
- Calculate the kinetic energy lost in the collision.
- Determine the period of oscillation for the block-clay-spring system.
When the oscillating block-clay-spring system reaches its maximum speed after the collision, will the spring be stretched from its original length by a distance greater than, less than, or equal to x0 ?
____ Greater than ____ Less than ____ Equal to
Justify your answer.
The collision is repeated using a rubber ball with the same mass as the ball of clay. The rubber ball is launched vertically with the same speed v0 . The collision between the rubber ball and the block is elastic. Will the speed of the block immediately after colliding with the rubber ball be greater than, less than, or equal to the speed of the block you calculated in part (d)i ?
____ Greater than ____ Less than ____ Equal to
Justify your answer.

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









